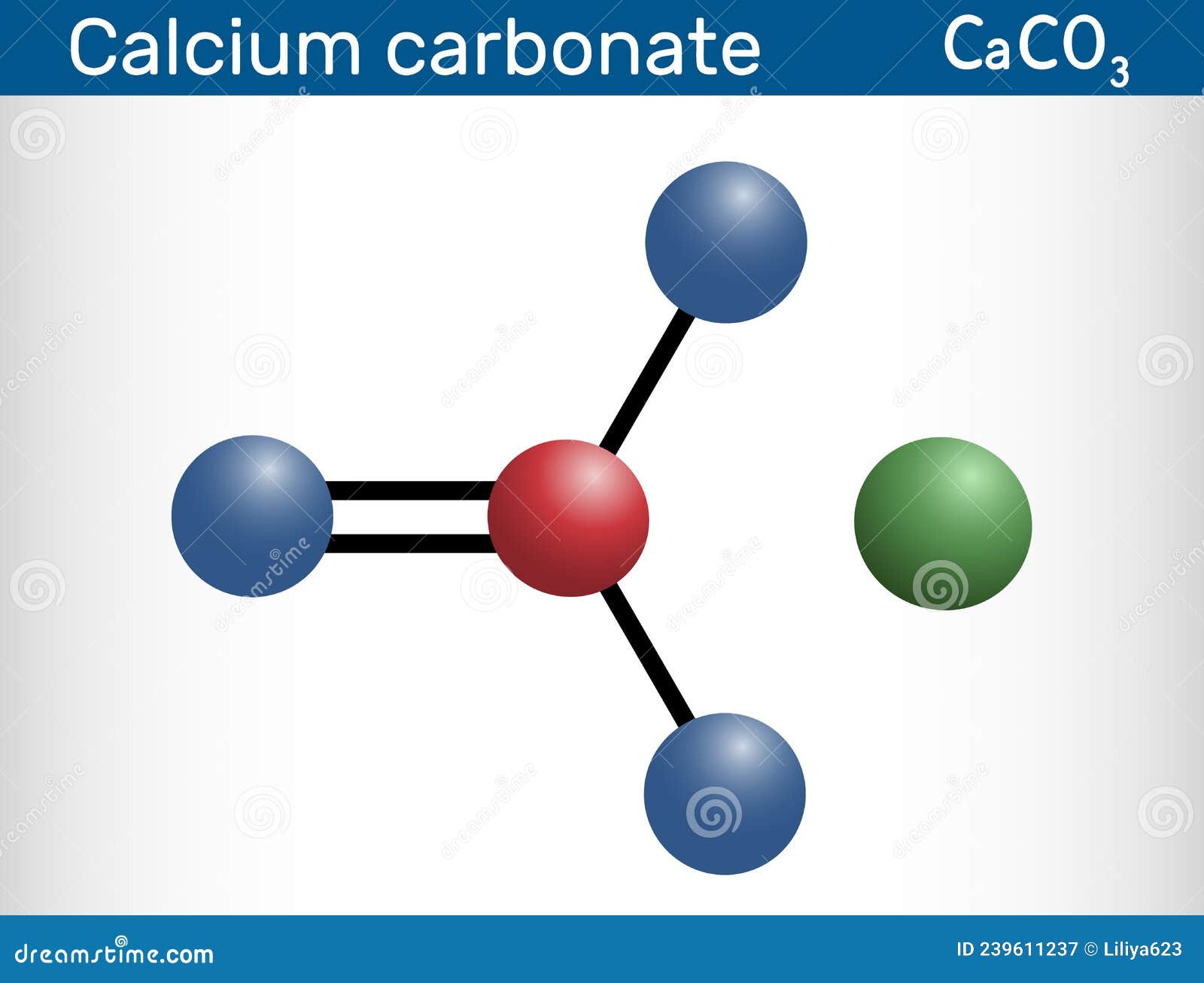
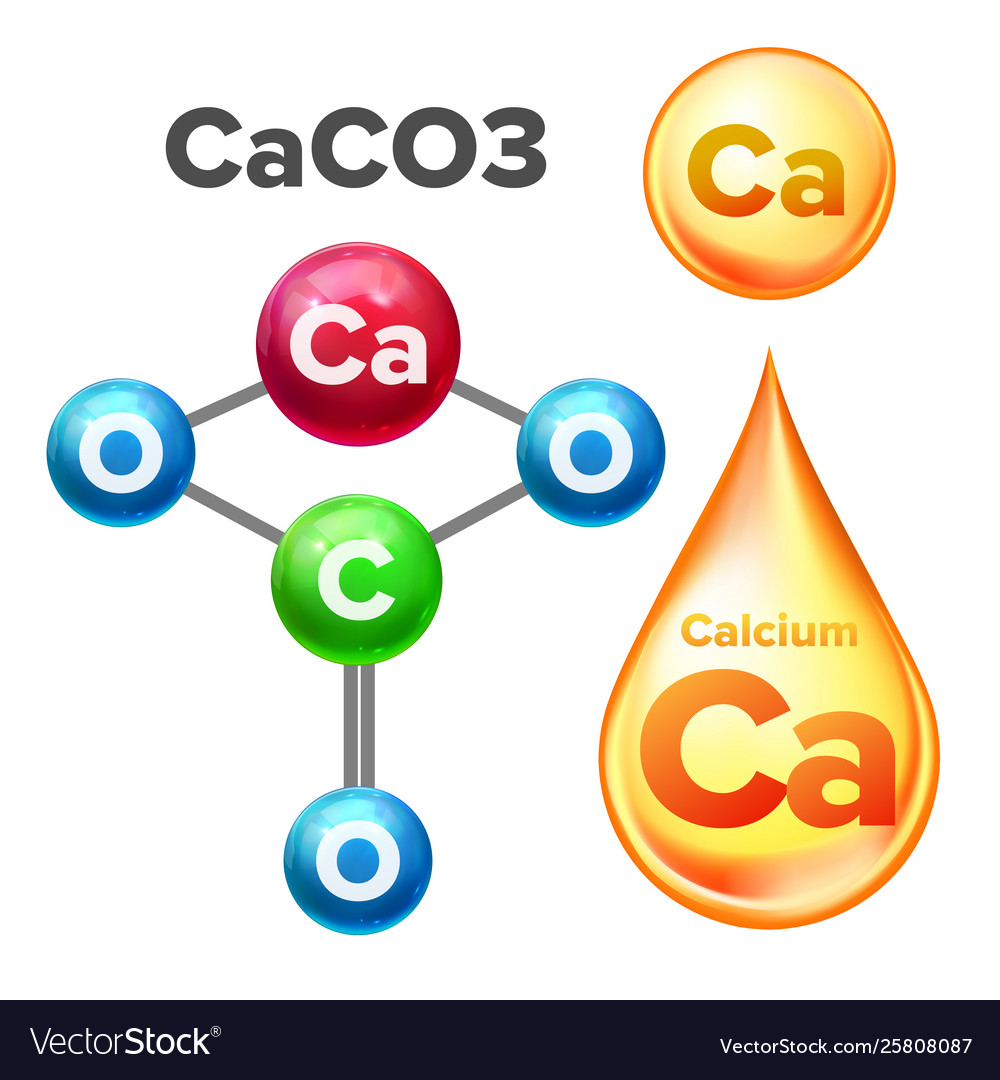
Calcium Carbonate Mineral Formation, Dissolution, Structures, & Geological Significance
Calcium carbonate minerals buffer the ocean's pH, provide protection to animals with CaCO3 skeletons or shells, provide homes to organisms that live in coral

Calcite : Properties, Formation, Occurrence and Uses Areas

Preparation of Calcium Carbonate

Calcium Carbonate Formation and Dissolution

How to Write the Formula for Calcium Carbonate

Science at Home: Vinegar and Calcium Carbonate

Science at Home: Vinegar and Calcium Carbonate

Lecture: From atoms to minerals: how calcium carbonates form and why we should care
7 Sedimentary Minerals and Sedimentary Rocks – Mineralogy

13 - Deep sea sediments

Magnesium Carbonate: 3D Ionic compound

Ion Pathways in Biomineralization: Perspectives on Uptake, Transport, and Deposition of Calcium, Carbonate, and Phosphate

Carbonate Minerals - an overview
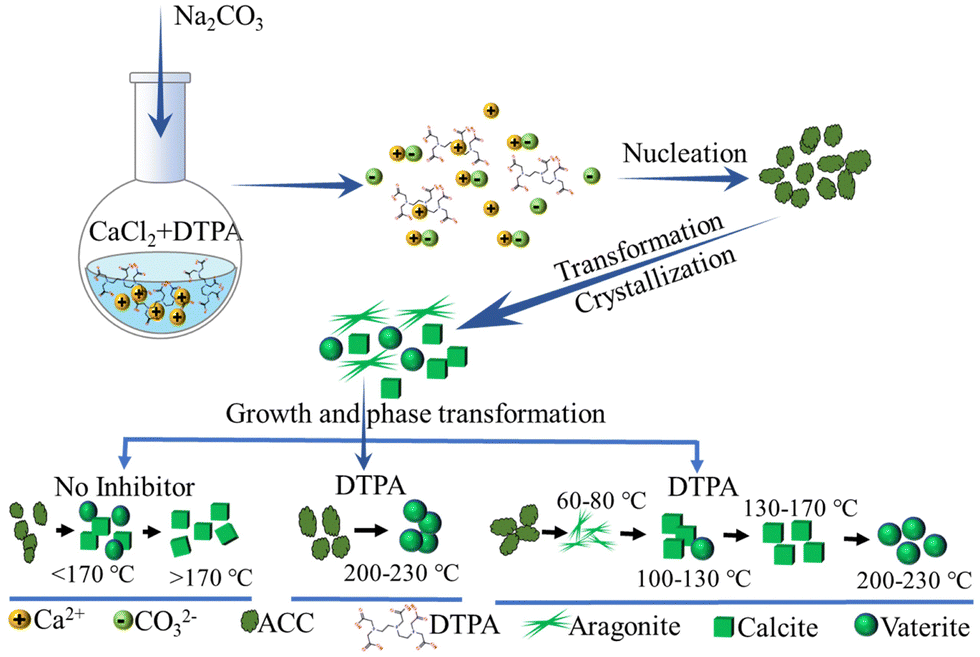
Calcium carbonate: controlled synthesis, surface functionalization, and nanostructured materials - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1CS00519G

Calcium carbonate cycle