Thermoplastics :: PlasticsEurope
Thermoplastics are defined as polymers that can be melted and recast almost indefinitely. They are molten when heated and harden upon cooling. When frozen, however, a thermoplastic becomes glass-like and subject to fracture. These characteristics, which lend the material its name, are reversible, so the material can be reheated, reshaped, and frozen repeatedly. As a result, thermoplastics are mechanically recyclable. Some of the most common types of thermoplastic are polypropylene, polyethylene, polyvinylchloride, polystyrene, polyethylenetheraphthalate and polycarbonate.

Semicrystalline Non-Isocyanate Polyhydroxyurethanes as Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Elastomers and Their Use in 3D Printing by Fused Filament Fabrication

Eight must-know notions about plastics

There's a not-so-great future in plastics., by Tommy Speigner

Thermosets and thermoplastics (adapted from PlasticsEurope [2020]).

Plastics consumption by end use application in Europe for 2007 (Simon

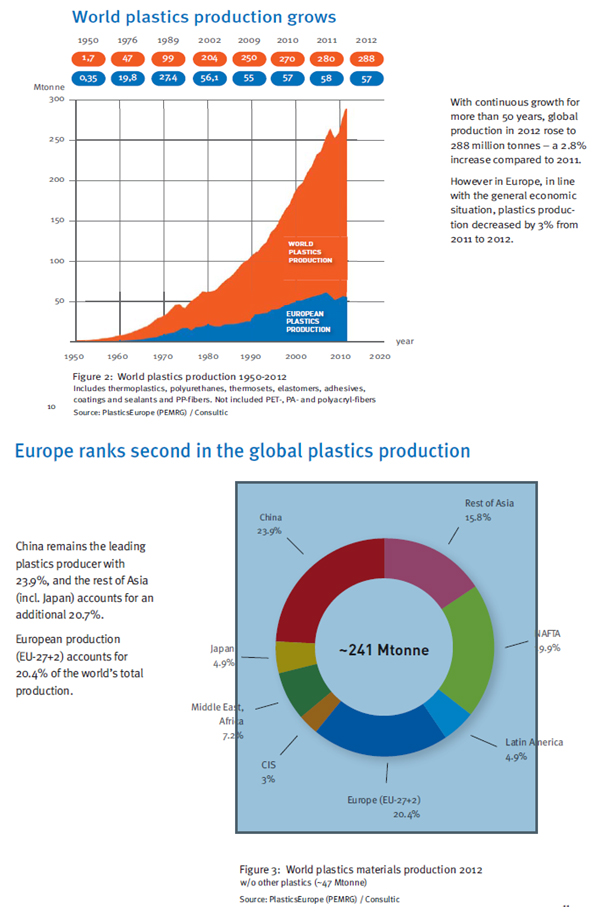
7.2: World plastics production 1950-2012. Includes thermoplastics

Recycling waste thermoplastic for energy efficient construction materials: An experimental investigation - ScienceDirect

Color for High-Performance Plastics

Europe: plastic production volume 1950-2021

A Review On Fabrication Techniques and Tensile Properties of Glass
Static polymer demand growth estimated in Europe for 2013

A large family • Plastics Europe









