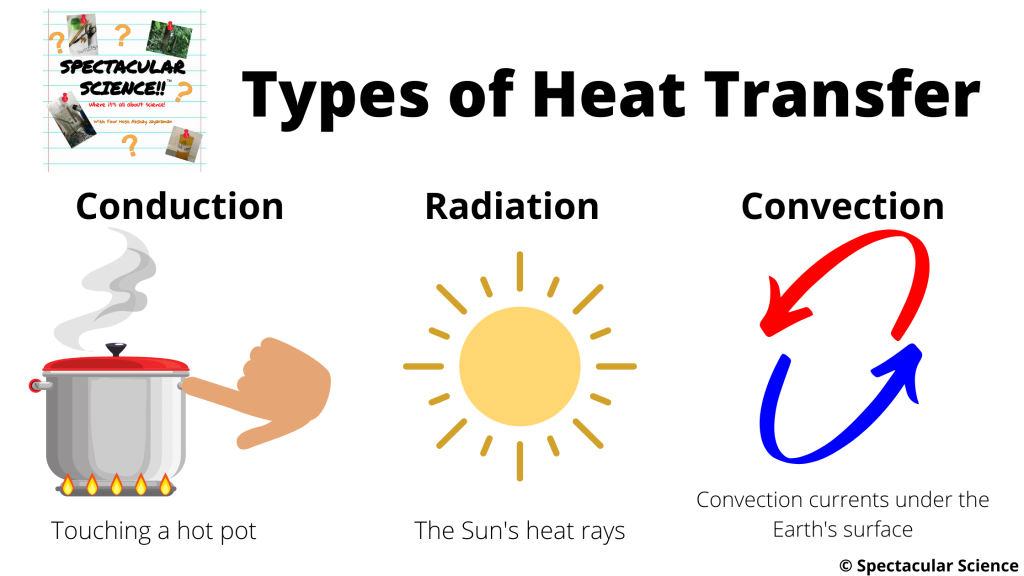
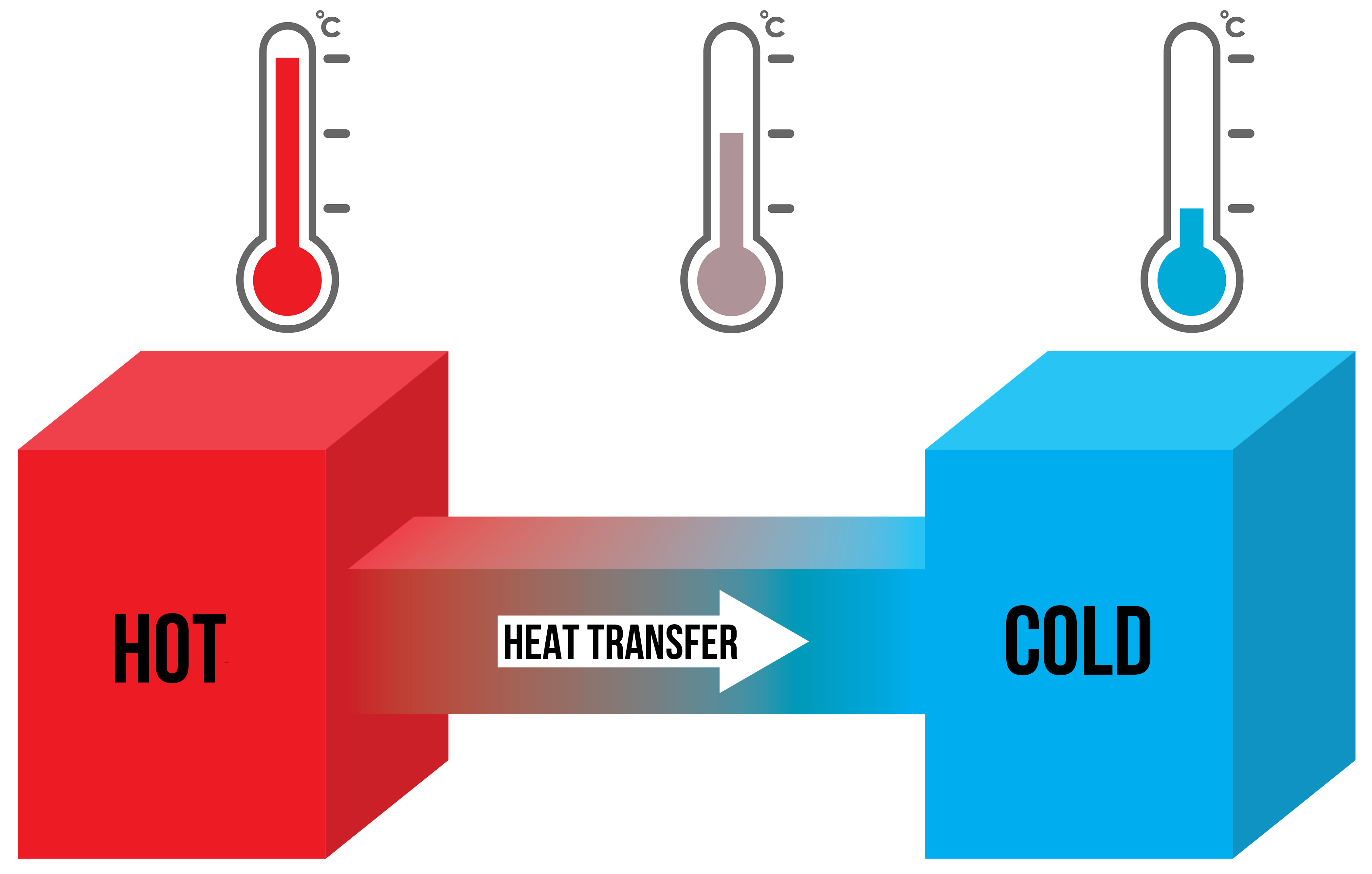
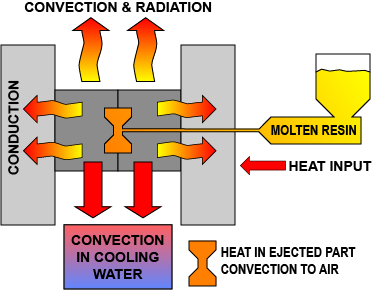
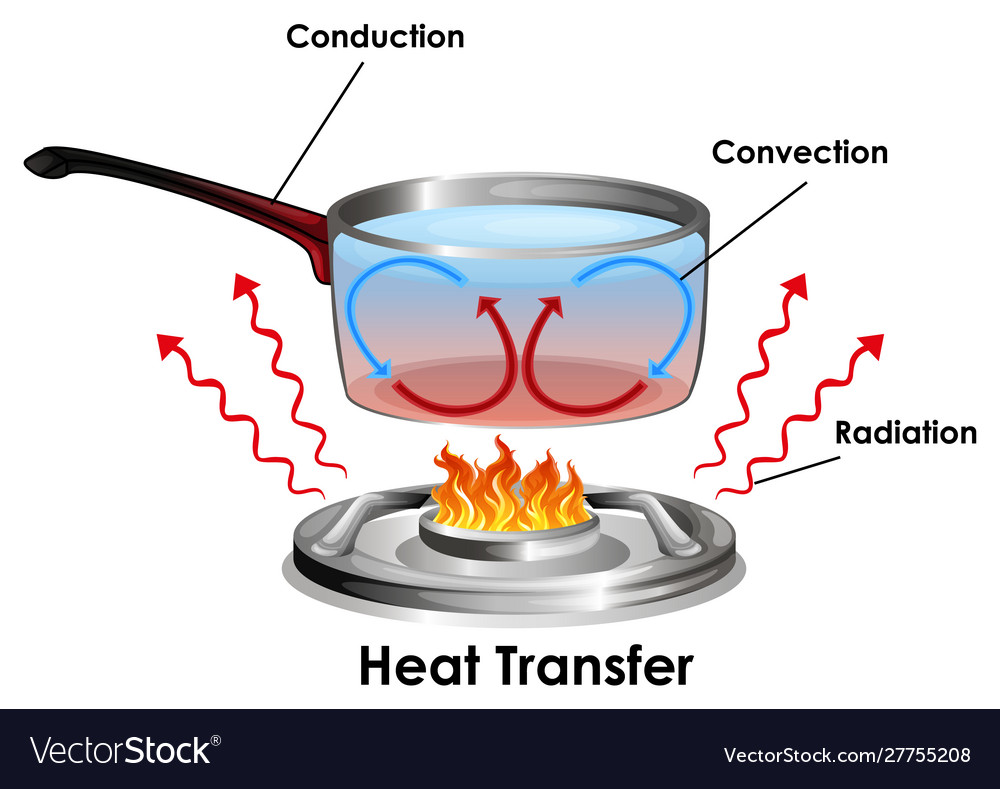
Heat transfer modes and domains used to model brain
Download scientific diagram | Heat transfer modes and domains used to model brain temperature Metabolically generated thermal energy is transported between the tissues, arteries, and veins by three heat transfer modes: conduction, advection (transport of thermal energy by a moving fluid), and convection (heat transfer from a flowing fluid to a wall resulting from combined effects of local conduction and advection represented by the local heat transfer coefficient). Energy and mass are conserved within each domain locally and globally across the whole brain and described by a system of equations (see “Methods” section). Red arrows represent the direction of blood flow and subsequent advection. Blue arrows represent conductive heat transfer from higher to lower temperature regions. Purple arrows that cross a vessel segment and intersected voxel represent the presence of convective heat transfer. The shaded (or darker) vessel segment or tissue voxel represents a higher temperature than the unshaded (or brighter) vessel segment or tissue voxel. from publication: Personalized predictions and non-invasive imaging of human brain temperature | Brain temperature is an important yet understudied medical parameter, and increased brain temperature after injury is associated with worse patient outcomes. The scarcity of methods for measuring brain temperature non-invasively motivates the need for computational models | Brain, Computational Biophysics and Biological Physics | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Clock Domain Crossing (CDC) - Semiconductor Engineering

Peter KOTTKE, PhD, Georgia Institute of Technology, Georgia

Andrei G. Fedorov's research works
How the Thermal Conductivity of Your PCB Substrate Affects Performance, Advanced PCB Design Blog

PDF) Personalized predictions and non-invasive imaging of human

Heat Transfer Modeling: An Inductive Approach SpringerLink, 44% OFF

Advances in Deep Learning-Based Medical Image Analysis

Translational control in aging and neurodegeneration - Skariah - 2021 - WIREs RNA - Wiley Online Library

Heat Transfer Modeling: An Inductive Approach SpringerLink, 44% OFF

Translating Functional Connectivity After Stroke: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detects Comparable Network Changes in Mice and Humans
Toward more efficient computing, with magnetic waves, MIT News